本报告为转载!
Reported by Greenwave Ropetec Co. Ltd. (irata member: 3166/T) 綠海訓練
Author(作者): Jay Chen 陳彥杰 (Technical Consultant of Greenwave 綠海訓練技術顧問)
(Illustrator畫圖者: Yi-Chang Su 蘇益璋)
- Time of accident 事故發生時間: February 24, 2025, 1:20 PM
- Location of accident 事故發生地點: Tainan City, Taiwan
- Technology used in the accident事故發生使用技術: Rope Access (Double Rope Technical)
- The work tasks being performed at the time of the accident 事故發生時的工作項目:
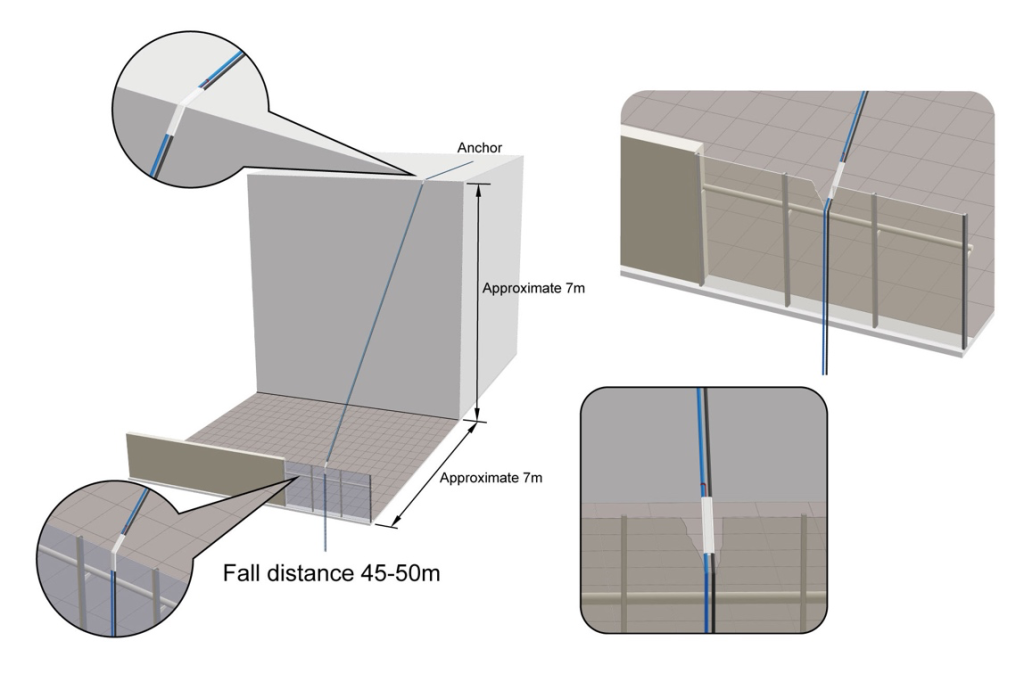
Building exterior cleaning 大樓外牆清洗 - Height level of accident 事故發生高度: 14F, Approximately 45-50 meters 大約45-50 公尺
- Height level of glass parapet wall 玻璃女兒牆位處高度: 15F, Approximately 45-50meters
- The main cause of the fall accident 墜落事件發生主要原因:
7.1 Excessive compression angle of the rope leading to the breaking of the glass parapet wall
繩索擠壓夾角過大導致玻璃女兒牆破裂
7.2 Broken glass severed the rope 破碎的玻璃切斷繩索
Description 說明
Based on the photos and videos circulating on the internet, as well as our conversation with the personnel who arrived at the scene that day, we gained an understanding of this accident. I would like to report a rope access fatality that occurred in Taiwan on February 24, 2025. The technician fell from the 14th floor. At the time, his ropes were squeezed against the glass wall. The exact angle of deviation is unknown, but based on the photos, it appears to be around 45 degrees. Later, due to the excessive pressure, the glass broke, and the rope was cut by the shattered glass. As a result, both ropes snapped, causing the fall and subsequent death. The technician was a Taiwan rope access local association Level 3, and the company he worked for was not an IRATA member.
根據網路傳出的照片以及影片,也加上我們與當天抵達現場人員的對話暸解,我們想要報告一個 2025/2/24發生在台灣地區的繩索上的死亡案例。技術員是從14F 墜落。當時他的繩子擠壓在玻璃 上,確切偏離角度不知道,但從影片看出來,似乎介於45度左右,後來由於擠壓力量過大,造成 玻璃破裂,繩索受到破裂的玻璃切割後,瞬間兩條繩索斷裂造成墜落而身亡。技術員級別為台灣 當地工業繩索技術協會三級,所屬公司非IRATA會員公司。
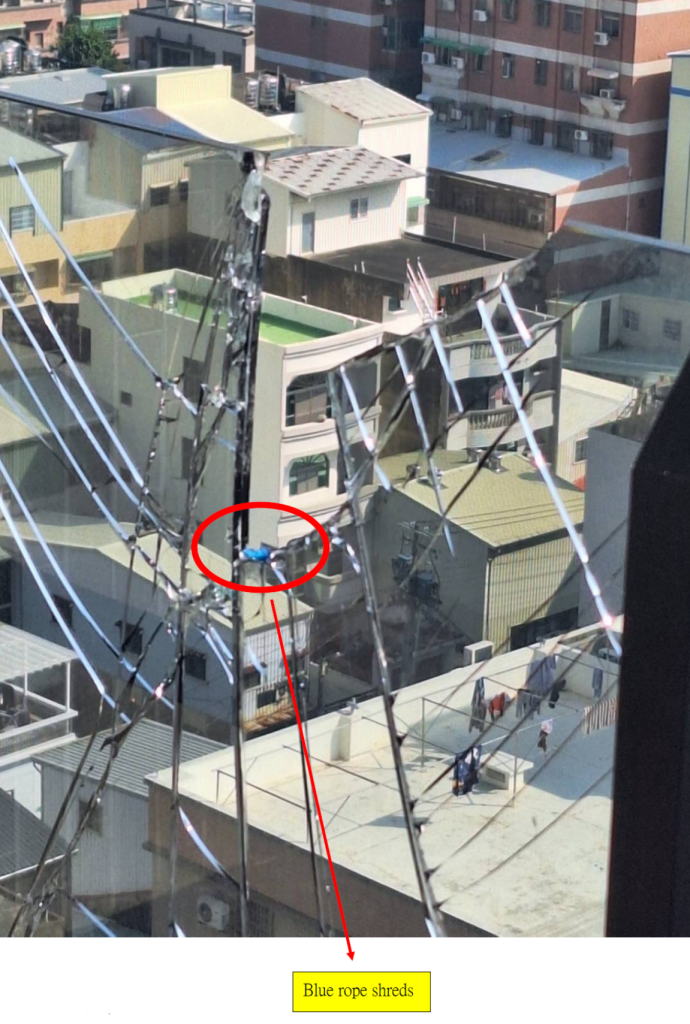
There was only one rope protector covering both ropes. The securing cord of the rope protector is placed on the safety rope (the black rope is the working rope, and the blue rope is the safety rope). However, in our judgment, even if there were two rope protectors, each covering one rope, this case would still result in both ropes being cut.
只有一個保護套包在兩條繩索。保護套的固定細繩是放在安全繩上(黑色繩索是工作繩、藍色繩索 是安全繩)。然而我的判斷,儘管是兩個保護套分別包在兩條繩索上,這個案例依舊會把兩條繩索 全部切斷。
Cause of occurrence 發生原因
The position of the rope protector is at the top edge of the glass wall. After the glass is squeezed and shattered, the funnel-shaped bottom of the glass forms very sharp edges. When the rope enters the funnel-shaped break in the glass, the length of the rope protector is insufficient to cover the rope. As a result, the working rope is cut first, almost instantaneously. When the weight shifts to the safety rope, the safety rope is also immediately cut and broken. From the video, it can be seen that the cut rope, including the rope protector, bounces back to the platform above. In Photo C, it can be seen that both ropes have bounced back to the platform, including the rope protector.”
繩索保護套的位置處於玻璃的最上緣,當玻璃被擠壓破裂之後,漏斗狀的玻璃底部出現非常銳利 的邊緣,當繩索進入漏斗狀玻璃破裂點的時候,剛好保護套的長度無法保護到繩索,因此工作繩 首先被切斷,幾乎是瞬間的時間,重量轉移到安全繩後,安全繩也跟著馬上被切割斷裂。從錄影 帶可以看到,被切斷的繩索包括保護套回彈回去上面的平台。照片C可以看到兩條繩索都回彈至 平台上,包括那個繩索保護套。
Control methods 控制方法
For the risks generated by hazardous factors, we should manage them using the RAP principle. The RAP stands for Remove, Avoid, and Protect, which represents the sequence of management strategies. In other words, if removing the hazard cannot be achieved, we should manage the risk by avoiding the hazard. If avoiding the hazard is also not feasible, the last resort is to manage the risk using protection methods.
對於危害因素所產生的風險,我們應該使用RAP原則加以管理,所謂的RAP指的是移除Remove, 避開Avoid, 保護Protector,這是管理招數的順序,也就是說,當使用移除危害因素致這個方式無 法達成時,我們應該使用避開危害因素的方式進行風險管理,如果也無法使用避開法,最後一個 手段才是用保護的概念去管理這個風險。
Below are the management strategies we recommend for this accident 以下是我們針對這個意外事故 建議的管理方式:
A. Removing the hazard 移除危害因素: Remove the glass parapet wall, and reinstall it after the work is completed. 將玻璃女兒牆拆除,等到工作結束之後再裝回去。
B. Avoiding the hazard 避開危害因素: There is a very large concrete structure directly above the glass parapet wall. The rope can be thrown over this structure, making the contact angle between the rope and the glass parapet wall nearly 0 degrees, meaning no compressive force will be applied to the glass. If a large protective mat is placed on the glass and rope protectors are added to the rope, this setup can effectively avoid accidents. 玻璃女兒牆的正上方有一個非常巨大的水泥結構,繩 索可以從那個結構物上方拋過去,這樣繩索與玻璃女兒牆的接觸夾角幾乎是0度,也就是不會 對玻璃女兒牆產生任何的擠壓力量,就算有也是非常非常的小。只要在玻璃上蓋上一塊大型保 護墊,並且也在繩索上加上保護套,這樣的架設方式是可以有效避免意外的發生。
C. Protecting the hazard保護危害因素: If neither option A nor B is implemented, and the original setup is maintained, meaning the compressive angle is about 45 degrees, any attempt to protect the rope might be futile, and the risk will still be very high. However, if the rope setup can be altered to reduce the compressive angle to very small, it may be worth considering placing an angle steel on top of the glass parapet wall, covering it with a large protective mat or even a thick blanket. This would reduce the direct compressive force on the glass, and once the compressive pressure is dispersed, the likelihood of the glass breaking will be minimal 如果不執行上述的A或是B的方 式,依舊維持原來這樣的架設,也就是擠壓夾角是45度左右時,那怎麼樣去做繩索保護都可 能是徒勞無功的,或者說風險依舊很大。但如果可以改變繩索架設,使其擠壓夾角很小時,那 就可以考慮使用角鋼放置在玻璃女兒牆的上緣,並且蓋上大型的保護墊,甚至是厚棉被,這樣 就可以降低繩索直接擠壓玻璃的壓力,而一旦擠壓壓力被分散掉,玻璃會破的機會就微乎其微了。
Photograph of the Accident Site 事故現場照片
Photo A
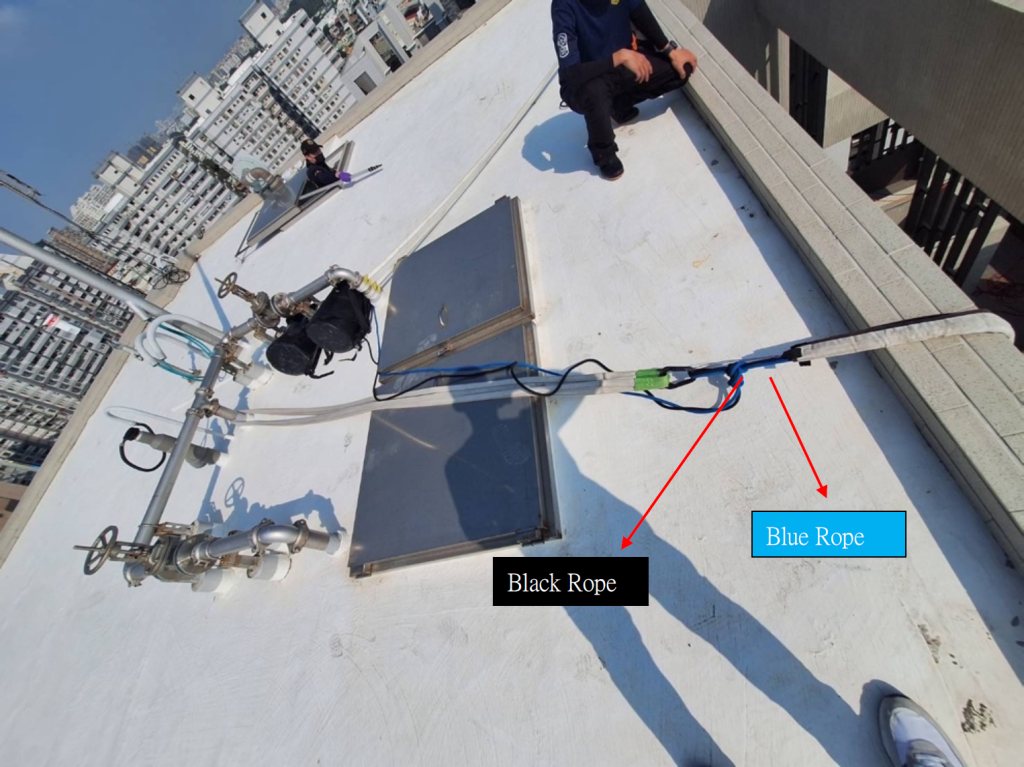

Photo B

Photo C
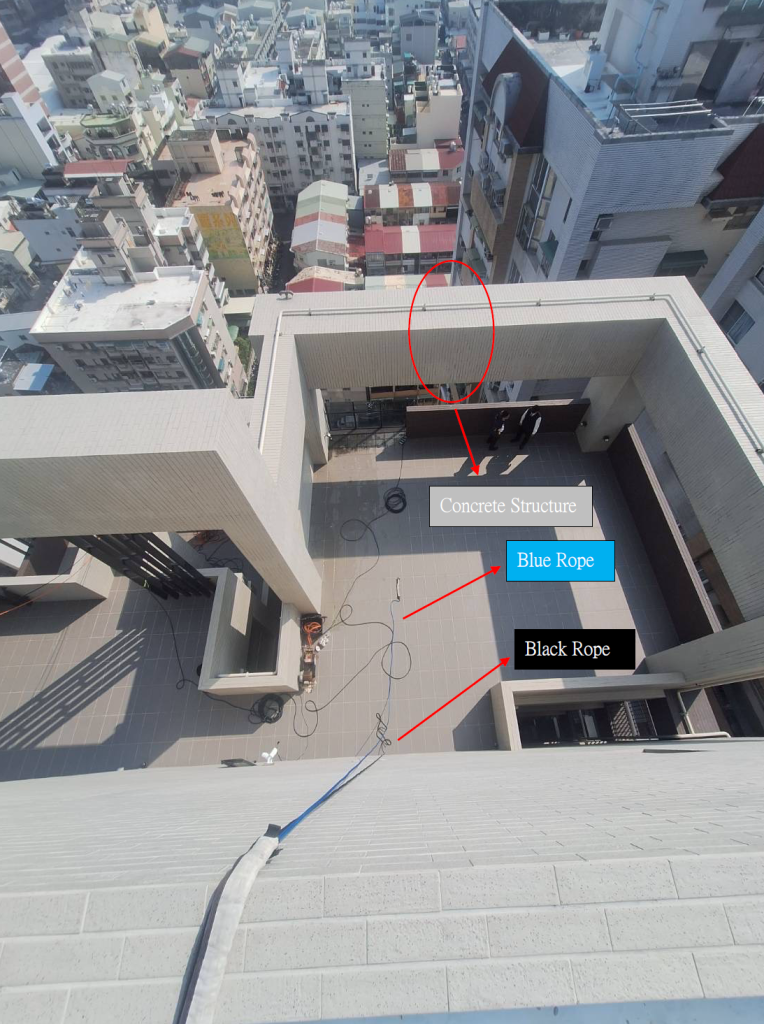

Photo D
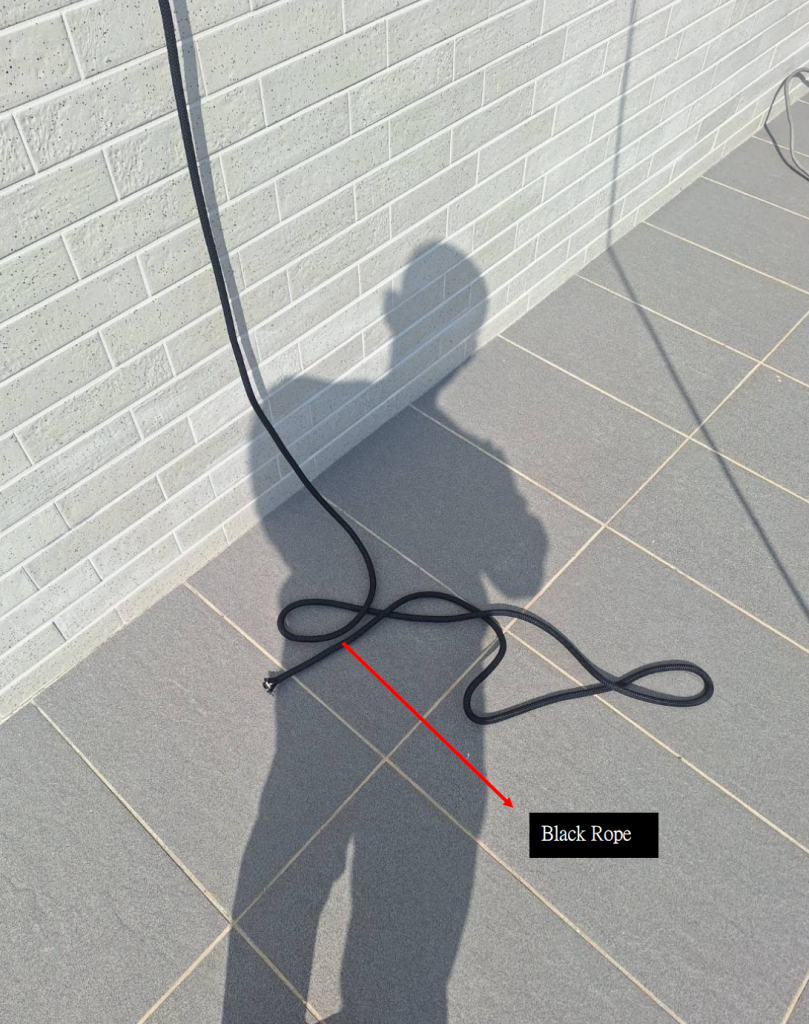

Photo E
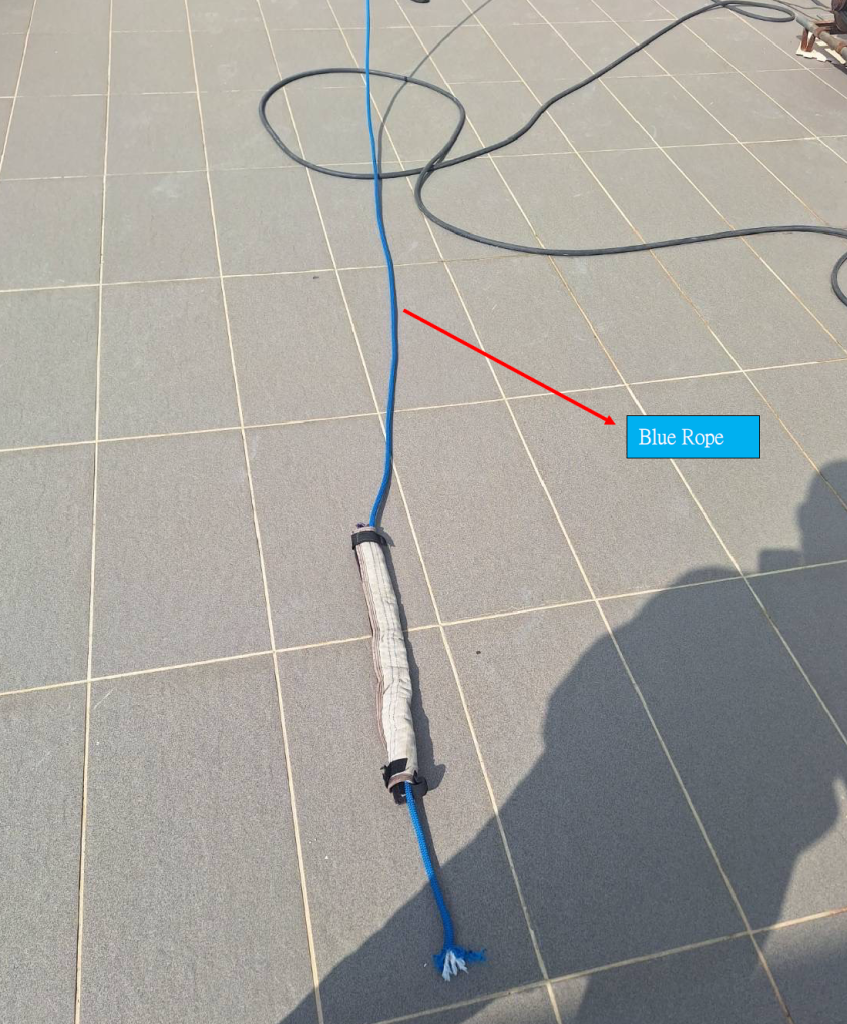

Photo F
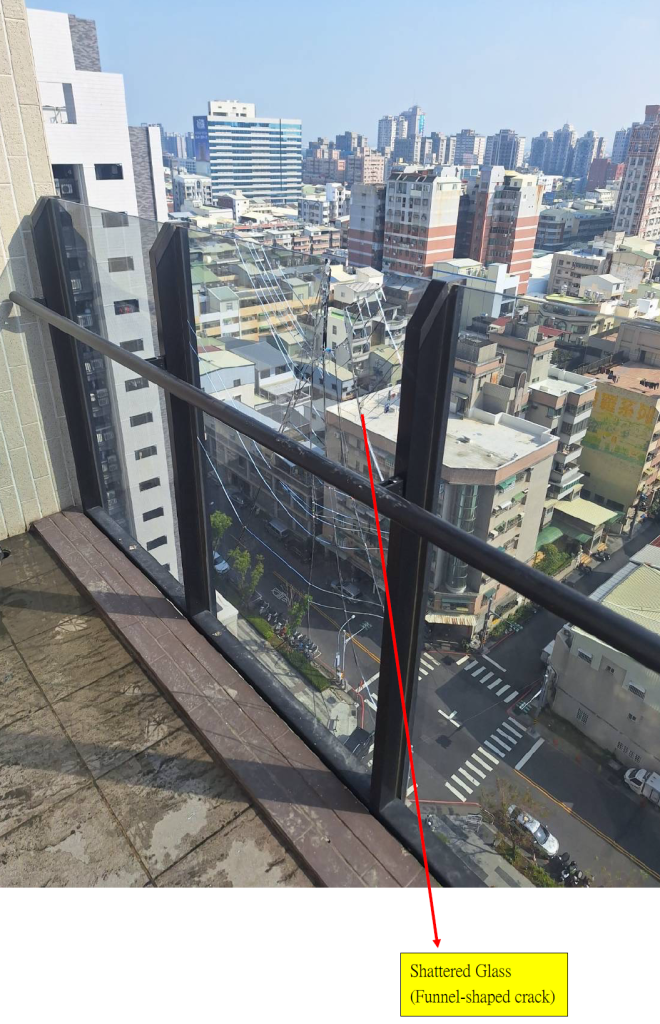

Photo G
